Diseases
Crop and livestock diseases can be caused by bacteria, fungi, nematodes, viruses, mycoplasmids, and other microorganisms. In order for disease of a crop or animal to occur:
- The pathogen must be present;
- The host must be susceptible to the pathogen; and
- The environment must be conducive to infection.
In conventional agriculture, disease treatment has been primarily focused on diminishing or eliminating the pathogen with allopathic compounds. In sustainable agriculture, the focus moves to modifying the environment (e.g., rotational grazing to avoid parasitic worms or pruning fruit trees to promote rapid drying of leaves and fruit) and reducing the susceptibility of the host (e.g., choosing disease-resistant crop varieties or adding probiotics to livestock feed). If allopathic compounds are employed in sustainable agriculture, they are often of “organic” origin, rather than synthetic.
The following practical ATTRA resources will help you learn strategies for managing disease sustainably.



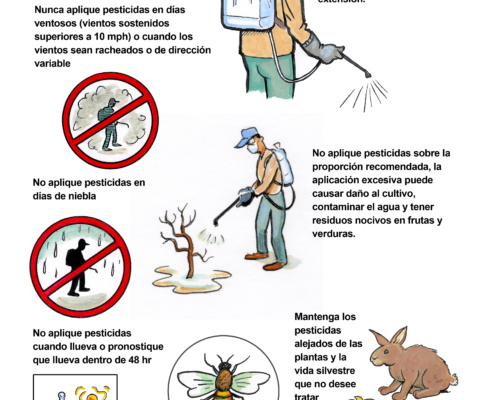
 Julian Fong Wiki Commons
Julian Fong Wiki Commons
 NCAT
NCAT NCAT
NCAT



